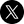Minimum Wyoming car insurance
Wyoming requires only one type of auto insurance: Liability insurance. Drivers must have liability insurance in order to legally drive. But there are other important insurance choices to consider. You don't want to be hit with surprise bills after a car accident. Here's a look at what's available in Wyoming so you can make good insurance picks.
Minimum liability insurance:
Liability insurance pays for damage and injuries you cause others. If you buy only minimal liability coverage, you can still be sued for car accident bills that your insurance doesn't cover. In Wyoming you must have liability coverage limits of at least:
- $25,000 bodily injury per person.
- $50,000 bodily injury per accident.
- $20,000 property damage per accident.
This is usually written as 25/50/20.
Uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage:
UM/UIM pays for your medical bills -- up to the limits you choose -- if you're hit by a driver who has no liability insurance or not enough.
- Car insurance companies in Wyoming must offer UM/UIM coverage but you can reject it in writing.
- If you buy UM/UIM, the minimum coverage is $25,000 per person/$50,000 per accident. This is for injuries, not car damage.
Medical payments (MedPay) coverage:
MedPay is available in Wyoming but not required. It covers medical bills and funeral expenses for those injured while riding in or driving your car. It doesn't matter who was at fault. It also covers you if you're hit by a car while walking.
Comprehensive coverage: Not required by the state, but if you have a car loan or lease you probably are required to have it. Comprehensive insurance covers the theft of your car or damage caused by hitting an animal, fire, vandalism, hail, flood, falling objects (including trees that hit your car) and explosions.
Collision coverage: Not required by the state, but if you have a car loan or lease you probably are required to have it. Collision insurance is for damage to your vehicle caused by hitting another car or an object, like a pole.
Rental reimbursement: Not required by the state. This pays a certain amount for a rental car if your vehicle is being fixed due to an accident.
You must show an insurance ID card (or other proof of financial responsibility) in Wyoming when:
- Law enforcement requests it.
- You renew vehicle registration.
- Your vehicle is involved in a car accident.
Penalties for not having car insurance in Wyoming
- First offense: fine between $500 to $1,500 and/or up to six months in jail.
- Second or subsequent offense: revocation of registration and license plates until a judge orders reinstatement
Source: Property Casualty Insurers Association of America
Complaints against the largest auto insurance companies in Wyoming
The Wyoming department of insurance tracks complaints against insurance companies that operate in the state. A "complaint ratio" number uses data from all states to show the level of complaints against a company relative to its size. Here are ratios for the biggest car insurance companies in Wyoming.
Car Insurance in Other States |
Updated Aug. 15, 2018